GHRP-2
GHRP-2 is a synthetic growth hormone secretagogue that binds to the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Research studies have highlighted its potential benefits, including promoting muscle growth, supporting immune function, and regulating sleep cycles. Notably, studies have also shown that GHRP-2 possesses oral bioactivity, allowing it to be effective when administered orally.
Product Usage
This product is intended for research purposes only. It is strictly designated for in vitro testing and laboratory experimentation. All information provided on this website is for educational purposes only. Any introduction into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. Only licensed, qualified professionals should handle this product. It is not a drug, food, or cosmetic and must not be misbranded, misused, or mislabeled as such.
What is GHRP-2?
GHRP-2, also known as pralmorelin, is a synthetic growth hormone secretagogue that activates the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor. As the first compound in its class, it is primarily used as a test peptide to assess growth hormone deficiency and secondary adrenal insufficiency. GHRP-2 has progressed through phase II clinical trials for potential use in treating short stature and is actively researched for its effects on appetite, muscle growth, immune function, and sleep regulation. Notably, GHRP-2 can be administered orally or sublingually, offering an alternative to injections for its therapeutic effects.
Structure
Sequence: D-Ala-D-2Nal-Ala-Trp-D-Phe-Lys
Molecular Formula: C45H55N9O6
Molecular Weigh:817.9749 g/mol
PubChem CID: 6918245
CAS Number: 158861-67-7
Code Number: KP-102, GPA-748, WAY-GPA-748
GHRP-2 Effects
1. Muscle Preservation:
Research on yaks has highlighted GHRP-2’s muscle-enhancing properties, primarily through increased protein deposition and reduced protein breakdown. In yaks experiencing growth plateaus due to food scarcity, illness, or harsh conditions, GHRP-2 effectively prevented muscle atrophy. It achieves this by inhibiting proteins like atrogin-1 and MuRF1, which regulate muscle degradation pathways. These findings suggest potential applications for preventing muscle loss in chronic conditions such as autoimmune diseases and cancer. Additionally, by stimulating growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), GHRP-2 promotes lean muscle growth even under challenging circumstances.
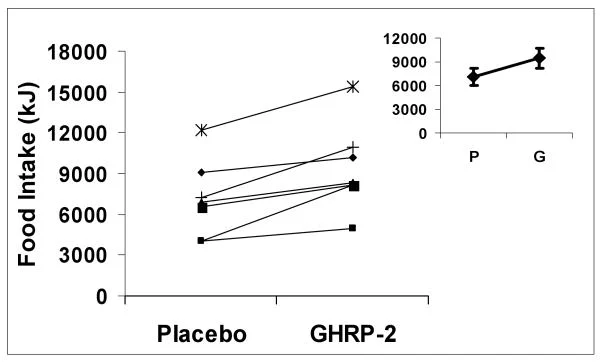
2. Appetite Stimulation:
GHRP-2 has been shown to significantly increase food intake, which can be particularly beneficial in managing chronic illnesses. A reliable appetite stimulant offers healthcare professionals a valuable tool for improving the nutritional status and overall prognosis of long-term patients.
3. Cardioprotective Properties:
Studies on fetal heart cell cultures suggest that GHRP-2, along with its analogues GHRP-1 and GHRP-6, can protect heart cells by reducing apoptosis (programmed cell death). This is especially important in heart attacks, where reduced blood flow makes heart cells highly vulnerable. Research on the GHRP-2 analogue Hexarelin suggests the existence of a specific receptor for these peptides. Identifying such receptors may aid in drug development and improve our understanding of heart health and disease prevention.
4. Immune System Support:
GHRP-2 has demonstrated potential benefits for immune function, particularly through its influence on heart cell preservation. By reducing cell death, it may contribute to a more resilient immune response and improved overall health.
5. Sleep Quality Enhancement:
GHRP-2 has been found to improve sleep by increasing the duration of deep sleep stages (stages 3 and 4) by approximately 50% and enhancing REM sleep by around 20%. It also minimizes sleep disturbances by up to one-third. These improvements contribute to better cognitive function, stable blood pressure, faster healing, and higher energy levels. While beneficial for all adults, these effects are especially valuable for older individuals who often struggle with reduced sleep quality due to aging. GHRP-2’s ability to optimize sleep may help individuals experience the benefits of a full night’s rest in a shorter timeframe.
6. Pain Modulation:
Initially, researchers believed GHRP-2 alleviated pain in osteoarthritis models by boosting growth hormone levels and accelerating tissue healing. However, further studies revealed that pain relief occurred before the healing process began, suggesting GHRP-2 directly influences pain perception. It acts on opioid receptors, which play a role in pain regulation. Unlike traditional opioids that affect all opioid receptors—leading to side effects such as respiratory depression and addiction—GHRP-2 selectively targets receptors responsible for pain relief and sedation. This selectivity presents a promising avenue for developing opioid-based pain treatments with fewer adverse effects.
DISCLAIMER: FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY
All articles and product details provided on this website are strictly for informational and educational purposes.
The product information presented here applies solely to in-vitro studies—experiments conducted outside of living organisms, such as in laboratory settings. These products are not classified as medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical conditions, ailments, or diseases.
Furthermore, the use of these products in humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law.

